At Staffice, we consider it important that you understand your payslip. Therefore, we want provide you some information about it.
General Details of the Worker
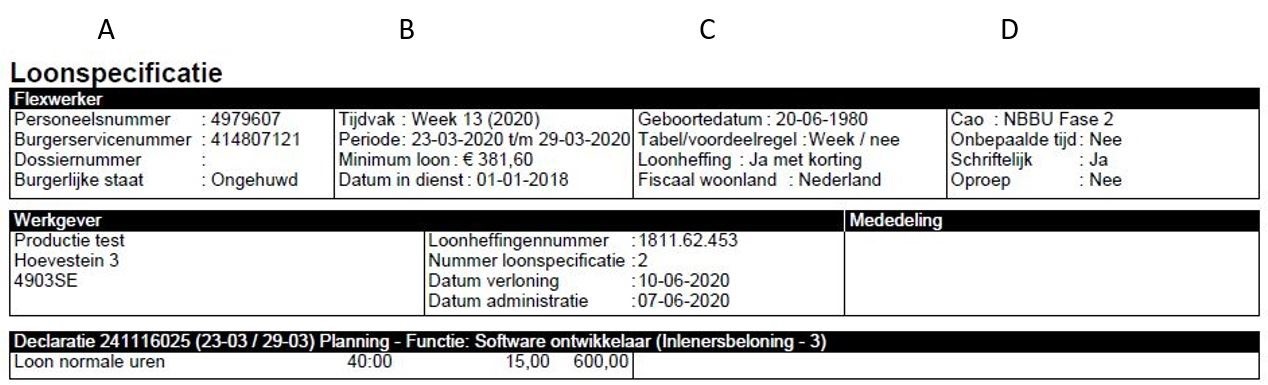
- Column A: This column displays your employee number (registration number), social security number (if provided), file number, and marital status.
- Column B: It shows the period during which you worked, for example, week, month, 4 weeks, or day. It also displays the corresponding period, minimum wage, and the date of employment. If the daily table applies, a payslip per week is generated, and the period is indicated as ‘Day 1 to 7’.
- Column C: Displays your date of birth, chosen wage period table, application of payroll tax, and your fiscal residency.
- Column D: Indicates your collective labor agreement (CAO) phase, whether it’s a fixed-term or indefinite employment contract, whether the employment contract is documented in writing, and whether it is an on-call agreement.
Declaration | General Details of the Hours Declaration
Columns A and B: These columns display processed salary components.
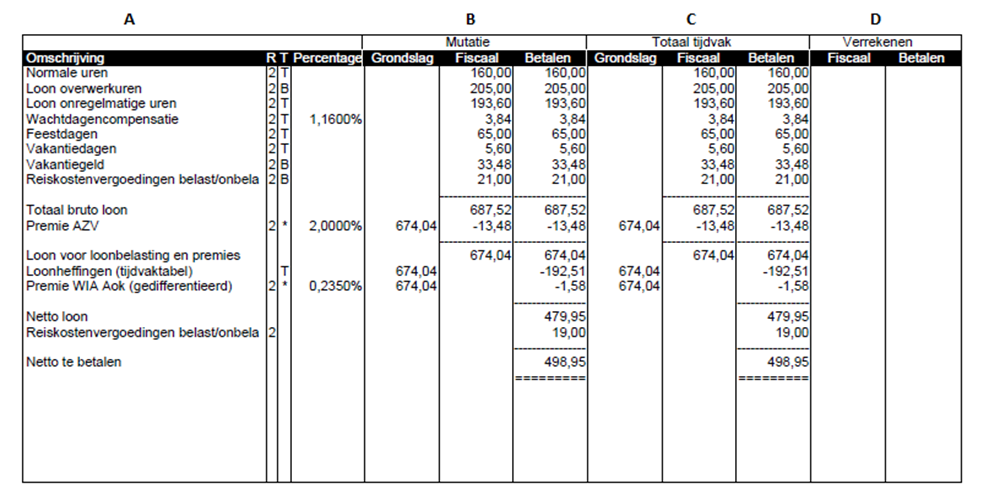
Column A
- Description: This column shows descriptions of components from the payslip, such as waiting day compensation, gross salary, and payroll tax. These components are used to calculate your net income.
- R: This is the risk group in which the respective line is processed, for example, 1 or 2. At the bottom, the cumulative values show which risk group corresponds to the displayed number.
- T: This column shows the tax table used for processing the respective line, denoted as T = Table (regular white table) or B = Special remuneration table (for example, for overtime hours).
- Percentage: If the percentage of the respective line is different from 100%, it is displayed here. For example, for Unemployment Insurance premium, Employee Contribution to Health Insurance, and Overtime Hours Pay.
Column B
- Mutation: This column shows the totals related to the mentioned hours, allowances, and deductions from processed declarations.
- Basis: This displays the bases on which the salary calculations are performed.
- Fiscal: This column shows the totals used for calculating payroll tax.
- Payment: This shows the actual income. After listing the net salary, there may still be deductions or allowances, such as offsetting an advance payment, wage garnishment, or paid travel allowances.
Column C
- Mutation: This column shows the totals related to everything processed in the respective wage period. If multiple salary payments have been made, it sums up the previously paid salary and the current payment (Column B).
- Basis: This displays the bases on which the salary calculations are performed. There are different types of wages listed on the payslip, such as ‘gross salary’, ‘salary for employee insurances’, and ‘salary for payroll taxes and contributions’. Each salary is the basis for a different type of payment. If multiple payments have been made in the same wage period, these amounts will not be equal to the bases in Column B.
- Fiscal: This column shows the totals used for calculating payroll tax. This usually matches the amounts in the ‘Payment’ column. However, differences can occur due to the fiscal addition of a car/bicycle or the withholding of WIA (Work and Income according to Labor Capacity) premium.
- Payment: This shows your actual income of the worker. After listing the net salary, there may still be deductions or allowances, such as offsetting an advance payment, wage garnishment, or paid travel allowances.
Column D
- Settlement: In these columns, reconcilable data is displayed. This can occur if payments have already been made after the current period. For example, when your week 20 is paid, the payments for weeks 21, 22, and 23 have already been settled. The payment of week 20 in this example can affect discounts received on premiums for weeks 21, 22, and 23. Changes in salary can also affect owed or paid premiums, such as overpaid or underpaid payroll taxes. This process follows the method of VCR (Rolling Cumulative Calculation).
- Fiscal: This column shows the totals used for calculating payroll tax. This usually matches the amounts in the ‘Payment’ column. However, differences can occur due to the fiscal addition of a car/bicycle or the withholding of WIA (Work and Income according to Labor Capacity) premium. This column always ends with salary for payroll taxes and contributions.
- Payment: This shows the actual income of the worker. After listing the net salary, there may still be deductions or allowances, such as offsetting an advance payment, wage garnishment, or paid travel allowances.
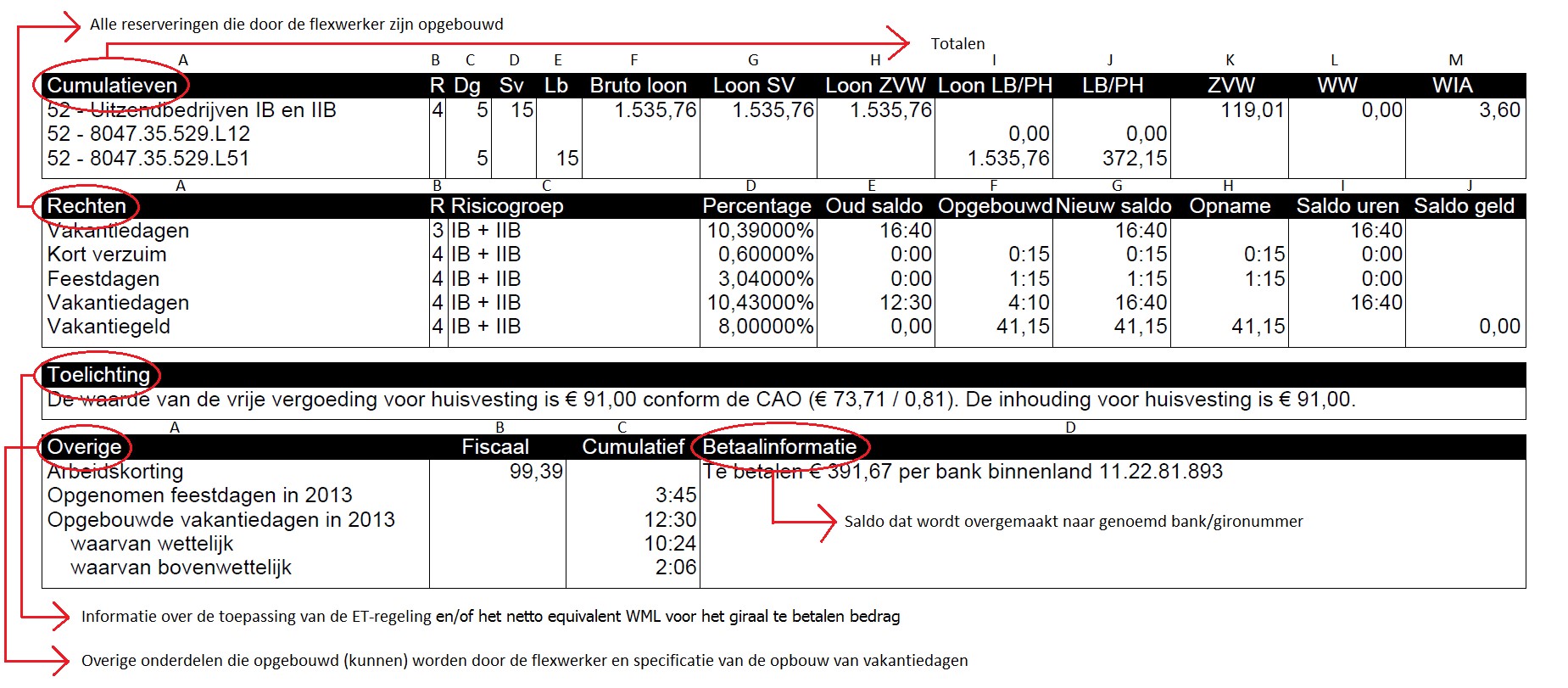
Cumulative Totals
The balances shown are valid on the day of payroll, not at the end of the processed wage period. For example, when your week 20 is paid, the payments for weeks 21, 22, and 23 have already been settled. The payslip of week 20 will display the amounts of previously paid weeks 21, 22, and 23 in the cumulative totals.
- Column A: Displays the risk group and payroll tax number.
- Column B: Shows the risk group in which cumulative totals are built within the wage period.
- Column C: The total number of paid days within the wage period.
- Column D: The total number of social insurance days, which count for social insurances.
- Column E: The total number of paid days for income tax purposes.
- Column F: The total gross salary.
- Column G: The total salary for social insurances.
- Column H: The total salary for the Health Insurance Act.
- Column I: The total salary for payroll taxes and contributions.
- Column J: The total amount withheld for payroll taxes and contributions.
- Column K: The total amount paid for employees’ contribution to Health Insurance Act.
- Column L: The total amount paid for Unemployment Insurance Act.
- Column M: The total amount paid for the Work and Income according to Labor Capacity Act.
Rights
- Column A: Displays the accrued reservations.
- Column B: Shows the risk group to which the rights apply, for example, 1 or 2.
- Column C: Displays the name of the risk group corresponding to the number in the first column, for example, IA or IIB.
- Column D: Shows the percentage of the reservation.
- Column E: Displays the old balance until the payroll date.
- Column F: Displays the accrued amount from processed hour declarations.
- Column G: Displays the new balance (old balance + accrued balance). This balance excludes any reservations taken.
- Column H: If there are reservations taken, the withdrawal amount is shown in this column.
- Column I: Displays the new total balance in hours, including any reservations taken.
- Column J: Displays the new total balance in money. This balance includes any reservations taken.
Explanation
The explanation is displayed on the payslip if the ET scheme is applied and/or the ‘Net Equivalent of Minimum Wage’ has been calculated. The explanation provides information about the ET scheme on the respective payslip and/or the minimum net (bank) amount to be paid.
Other
Column A: All other information such as savings plan and pension premiums are listed here. The basic pension is calculated based on all paid normal hours, irregular hours, increased hours, decreased hours, standby pay, and pay for disability.
More information about


























